Home > Achievement > Research Project Summary Report > 2017 year > The establishment and application of specific molecular markers for Fusarium crown and root rot resistance gene in tomato. Home > Achievement > Research Project Summary Report > 2017 year > The establishment and application of specific molecular markers for Fusarium crown and root rot resistance gene in tomato. |
The establishment and application of specific molecular markers for Fusarium crown and root rot resistance gene in tomato.
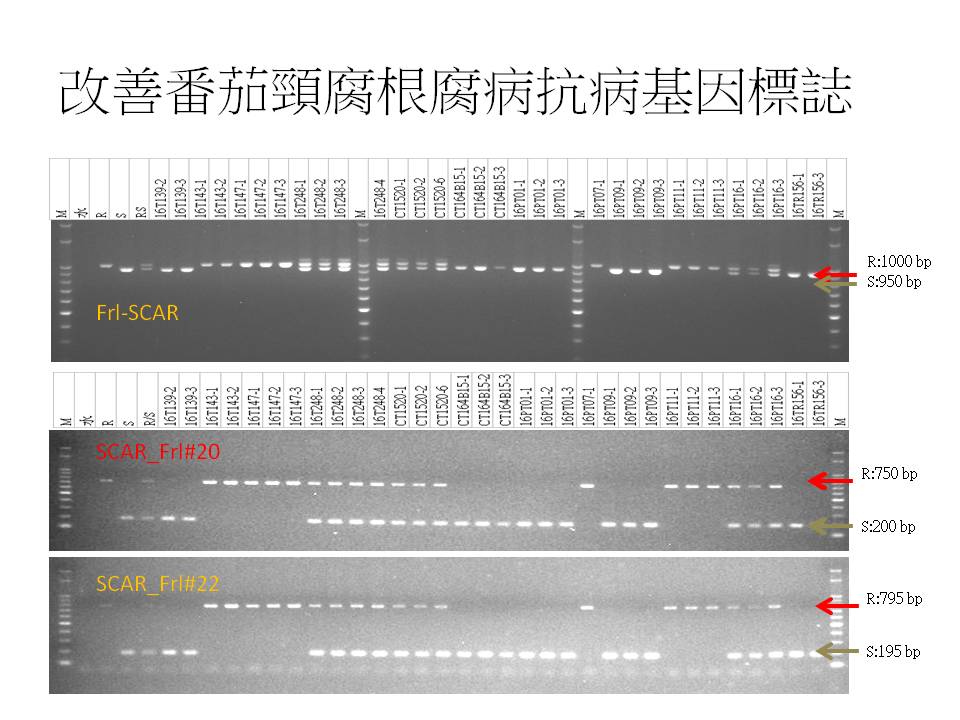
Tomato Fusarium crown and root rot caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. Sp.Radicis-lycopersici (FORL) is the most susceptible plant disease in tomato cultivated in greenhouse. The optimum growth temperature is 18 ℃ for FORL . After infection, the disease caused wilt death and reduced fruit quality. Tomato Fusarium crown and root rot was first discovered in Japan, then occurred in many countries and gradually formed a threat. At present, the CAPS marker in the literature report needs to undergo the enzymatic cleavage reaction. However, the SCAR marker is not easy to interpret due to the small difference of the fragments. In this study,primers were improved and redesigned as the SCAR-TSS-Frl # 20 marker.Through the testing of anti-susceptible materials from different sources,the band was amplified 750bp in resistant materials and 200bp in susceptible materials. The correlation coefficient was 94% between the test results and the interpretation of SCARFrl. The bands were clear and stable, easy to interpret and suitable for the industry.

▲Fig1. Tomato Crown Rot is a soil borne disease caused by
Fusarium oxysporum f. Sp. Radicis-lycopersici ( FORL) .
The optimum growth temperature is 18 ℃ for FORL. After
infection, the base of the stems and roots of plant are brown
and rotten, resulting inplantsdeath or reduction of fruit quality.
▲Fig2. The new Scar markers frl# 20 and #22 Improved disadvantages that amplified
band is too close and not easy to critical result. Correlation Coefficient between new
marker and original marker was up to 0.94, resulting in use of breeding industry.