Taiwan Seed Improvement and Propagation Station,MOA
 Home > Achievement > 2019 Research Project List > The establishment and application of specific molecular markers to detect bacterial spot resistance gene in tomato. Home > Achievement > 2019 Research Project List > The establishment and application of specific molecular markers to detect bacterial spot resistance gene in tomato. |
The establishment and application of specific molecular markers to detect bacterial spot resistance gene in tomato.
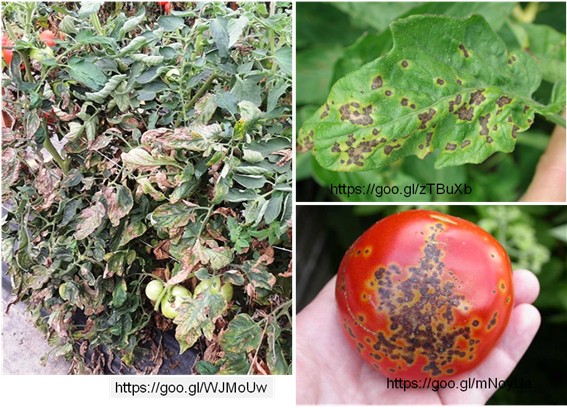

▲Fig. 1. Tomato Bacterial Spot is caused by the bacteria Xanthomonas spp. It can be transmitted by animals, humans, insects, agricultural tools, soil particles, water pollution, and so on. When growing in the high-humidity environment with a temperature of 24-30 °C, tomato is the most susceptible to this disease, which damages plants and fruits, and affects fruit quality and yield in some severe cases.
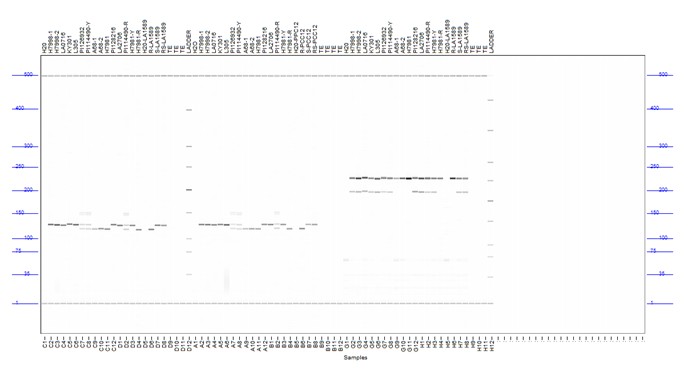
▲Fig. 2. Analysis of Capillary Electrophoresis of Tomato DNA Using InDel Marked PCC12 and dCAP Marked cLEC-24-C3G After PCR Amplification
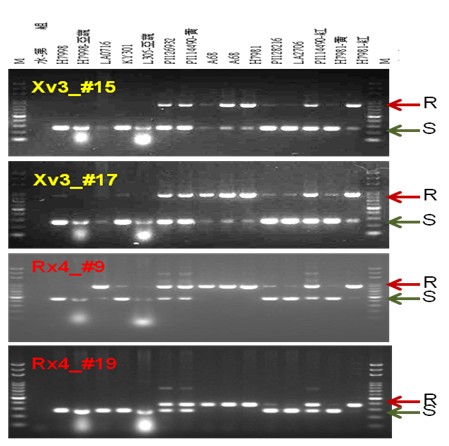
▲Fig. 3. Tomato DNA material with a newly developed SCAR mark, targeted to tomato bacterial spot disease race T3 resistance genes Xv-3 and Rx-4, horizontal electrophoresis after PCR amplification.
