- Promotion of demonstration sites for the recycling of tomatoes, mushroom media and tea by-products
- Promote to Popular Application of Intelligent Production and Sales Management in Vegetable Nurseries
- Research on Seedling Propagation Technology of Eastern Aboriginal Tribes
- Counseling on Digital Transformation of Small,Medium and Micro-sized Agricultural Operators of Crops and Seedlings with Potential for Export
- Construction of Environmental Verification System and Standards for Cucurbit Vegetables Nurseries
- Promotion of Taro Healthy Germplasm Conservation and Propagation System
- Research on the New Development Trend of Seed Treatment Technology
- Evaluation and Application of Drought-tolerant Potato Germplasm Resources
- Establishment the Biological Indicator of Disease Resistance for Tomato in Drought Condition
- Improvement on the Micropropagation Technique – In Vitro Propagation of Avocado (Persea americana Mill.) through Apical Buds and Nodal Segments
- Research on germplasm maintenance and industrial application of vegetative propagation crops
- Germplasm Development and Application of Aeridinae Orchids and Cattleya Alliance
- Research on Genetic Resources and Plant New Variety DUS Testing Techniques Management and Application of the Economical and Special Crops in Taiwan
- Next-generation Ark of Agriculture and Forestry Germplasm - Germplasm Regeneration of Important Cross-Pollinated Crops
- Establishment of organic seed production and supplying system for grain crops
- Techniques development for bulb flowers breeding
- Establishment of the HeatResistant Selection Index and Breeding of Tomato
- High Quality and Stress Tolerance Breeding in Tomato
- Establish Cucurbitaceae vegetable breeding technologies of heat tolerance
- Breeding of New Papaya Variety for the International Market
- Research on the behavioral intentions of Agricultural Social Responsibility of the trainees in Farmers' Academy
- Research on the Interpretation of AI Intelligent Distinctness, Uniformity and Stability (DUS) Test in Phalaenopsis
- Exchange and Cooperation on Propagation, Breeding Technology and Plant Variety Protection of Ornamental Bulbs and Medicinal Plants between Taiwan and South Africa
 Home > Achievement > 2023 Research Project List > Research on the New Development Trend of Seed Treatment Technology Home > Achievement > 2023 Research Project List > Research on the New Development Trend of Seed Treatment Technology |
Research on the New Development Trend of Seed Treatment Technology
(1) Research on Seed Treatment Regulations in Line with International Trends
Completion and Publication of the article "Introduction to Seed Industry Standards - A Case Study of Seed Propagation Systems in Taiwan, Japan, India, and Thailand." Referring to seed propagation systems in countries such as Japan and India, many similarities exist with Taiwan, primarily adopting a three-tier production system with requirements for field and indoor inspections. However, Thailand, particularly in the production of public rice varieties, has additional registration level requirements for certified seeds and different certification standards for commercial seeds compared to neighboring countries. Regarding the Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) chapter, it encompasses four major principles. The TBT agreement mandates that regulations formulated by WTO members should not be discriminatory, including national treatment and most-favored-nation treatment. For instance, if domestic seeds do not require inspection before being sold in the market, foreign seeds should not be subjected to this restriction either, ensuring no less favorable treatment than that given to domestic products, known as "national treatment." "Most-favored-nation treatment" means providing all other WTO members with the same treatment. For example, if seeds from the United States do not require inspection upon import, seeds from the European Union should also be exempt from inspection. In essence, non-discrimination ensures fair competition opportunities for domestic and foreign products. Additionally, according to the CPTPP agreement, chapters directly related to agriculture include: National Treatment and Market Access for Goods, Food Safety Inspection and Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS), Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT), Intellectual Property (IP), and Environment (a total of five chapters). In the TBT chapter, the main coverage includes (1) technical regulations related to product characteristics, processes, or production methods (mandatory standards), (2) standards (voluntary standards), and (3) procedures for demonstrating compliance with technical regulations or standards, such as testing, sampling, inspection, factory inspection, ISO 9000 quality management system, etc. Demonstrating conformity assessment procedures is an internationally recognized process in seed treatment regulations.
Currently, trade barriers between countries and Taiwan related to agricultural issues include investment, compliance with foreign acquisition and merger laws, inspection and quarantine, quarantine standard setting, standards and certification, rejection by other countries of laboratories issuing GLP standards, and import restrictions.
(2) Development of long-term protection technology on seed treatment for vegetables
This project involves four kinds of coating agents, including methyl cellulose, sodium alginate, xanthan gum, and arabic gum. These are combined with three chemical fungicides including azoxystrobin, procymidone and polyoxorim and three microbial preparations including Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (Ba), B. subtilis (Bs) and B. mycoides (Bm). The cucumber seeds undergo coating treatment to observe the preventive effects against Didymella bryoniae. The results indicate that the treatment groups with procymidone and polyoxorim at concentrations of 10X to 20X show better preventive effects compared to other treatment groups. As for microbial fungicides, Ba and Bs exhibit the highest inhibition rates, with all treatment groups achieving over 90%. Healthy cucumber seeds, after being treated with the coating agents, show germination rates ranging from 90% to 98% in each treatment group, with no negative impact on germination. The combination of chemical and microbial fungicides mixed with coating agents does not adversely affect the germination of the tested cucumber seeds. There is no observed inhibitory effect on seed germination with increasing test concentrations, and the normal seedling rate does not significantly decrease with higher concentrations.
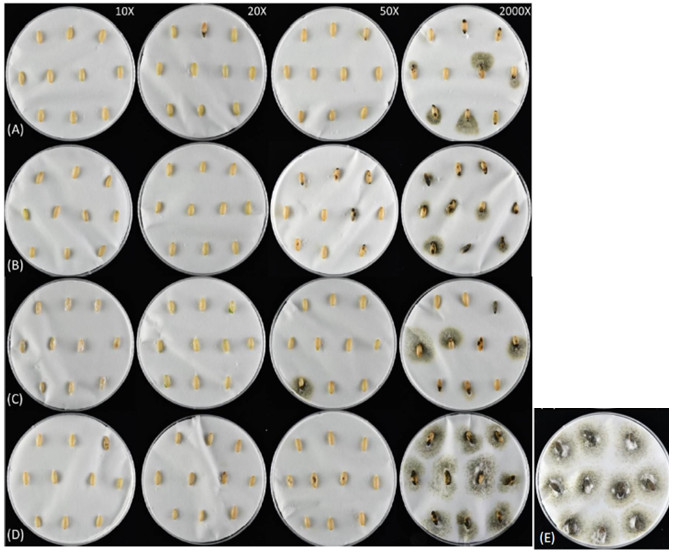 ▲Fig. 1. Different concentrations of permethrin fungicide mixed coating agent, including methylcellulose (A), gum arabic (B), sodium alginate (C) and xanthan gum (D), against courgette seed vine blight The prevention and control situations, from left to right, are the dilution concentrations 10X, 20X, 50X and the recommended dilution ratio. (E) is the control group. |
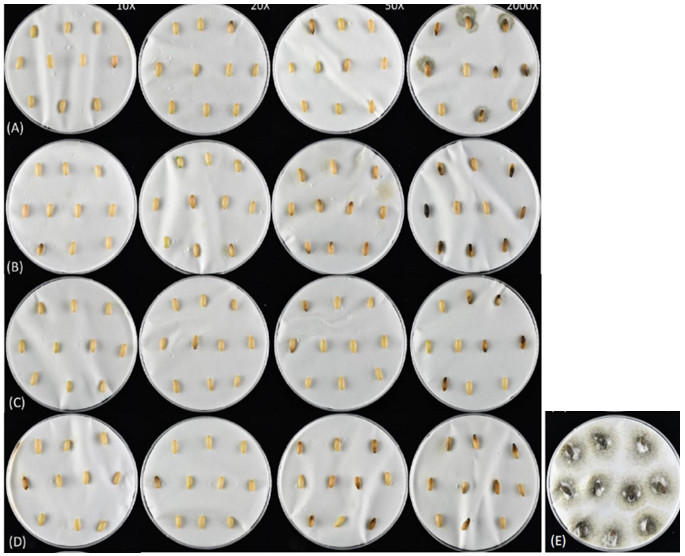 ▲Fig. 2. different concentrations of polymycin fungicide mixture coating agent, including methylcellulose (A), gum arabic (B), sodium alginate (C) and xanthan gum (D), on courgette seed vines The control conditions of blight, from left to right, are the dilution concentrations 10X, 20X, 50X and the recommended dilution ratios. (E) is the control group. |
(3) Research on complex seed treatment development
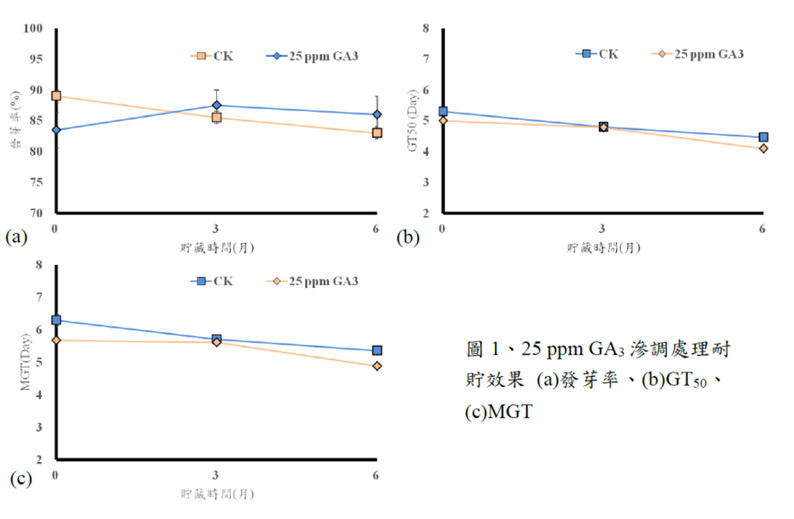
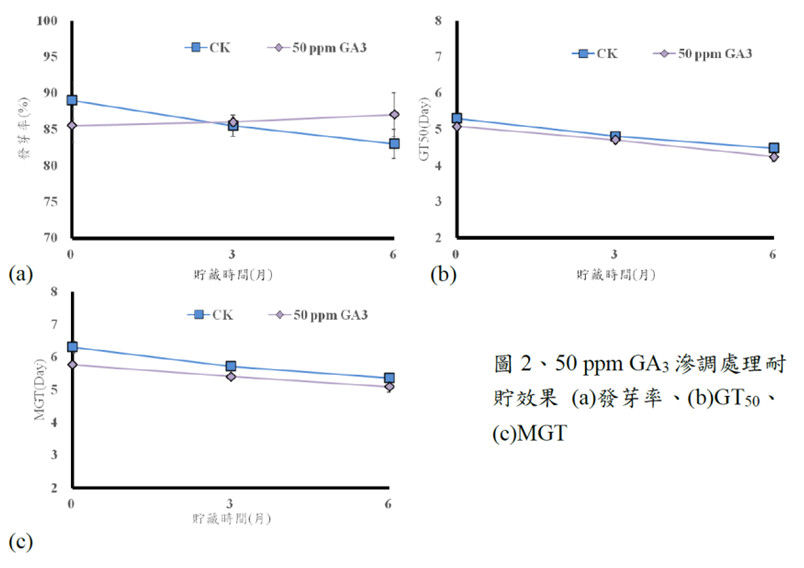
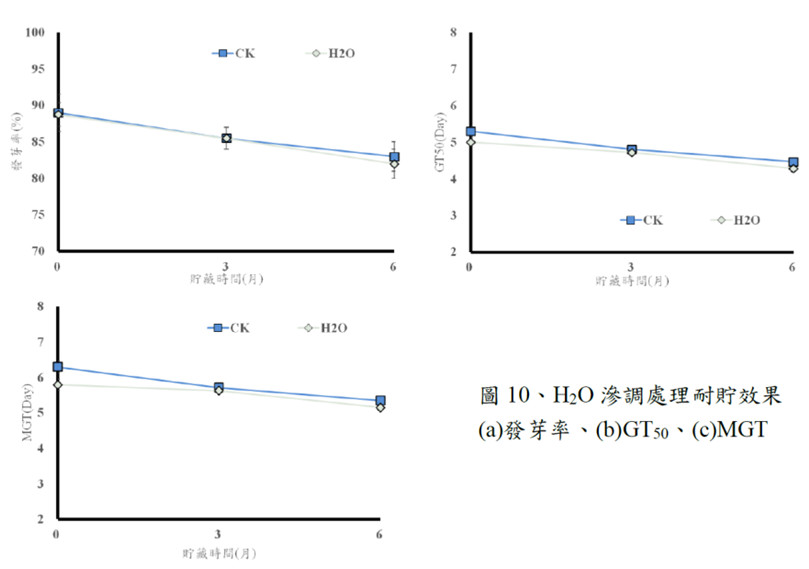
This year, we conducted a comprehensive test on the germination capabilities of two onion cultivars following ten different 12-hour priming treatments, subsequent to storing the seeds for six months. The results revealed that three specific priming treatments—25 ppm GA3, 50 ppm GA3, and H2O—were particularly effective in enhancing the germination of the two tested onion cultivars, showcasing a wide range of positive effects. In addition to the seed germination tests, our research extended to evaluating the mass production pelleting process of commercial onion cultivars this year. The results indicated that the germination quality of 'F1-706 Shenglu' onion seeds remained less affected after pelleting treatment, while the germination quality of 'F1-708 Shengsheng' onion seeds decreased after pelleting treatment. Despite observing a reduction and extension in GT50 and MGT days, the germination rate consistently exceeded 92%, rendering it suitable for industrial use.