- Application of Herbal Medicine Plants in Animal Feed additives and establishment of GAP production system
- Study on the Development and Industrial Value of Biochar which made by used medium of Mushroom
- Establish the molecular detection procedures for quarantine pathogens on important vegetable seeds
- Establishment of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers for resistance genes detection in tomato and purity testing of F1 hybrid watermelon seed.
- Construction of Parameterized Management Wisdom Network for Vegetable Nursery
- Application of production management information system in plant tissue culture
- Study on the optimization harvest period and extraction of Vitis thunbergii Sieb. &Zucc. var.taiwaniana
- Development of functional Products for anti-aging and eye-protection from dendrobium, and Vitis thunbergii var.taiwaniana
- The Establishment of Next Generation Sequencing technique to detect potato virus
- Establishment of environmentally friendly seed production system for grain crops
- System optimization and popularization of plant seedling joint marketing information platform
- Establishment of Detection Techniques for Seedborne Pathogens of Tomato
- The establishment and application of specific molecular markers to detect bacterial wilt resistance gene in tomato.
- Determinant RNA detection of Bacterial spot of Tomato
- Development for multiple refined processing techniques to promoting seed quality
- Resistance breeding and industrial applications of anti-wilt for cucurbits and eggplant rootstock
- Establishment of highly effective isolated facility for healthy seedling
- Development of potyvirus resistance in melon using CRISPR/Cas9 technology
- The study of healthy seedling production by in vitro micropropagation
- The establishment and application of specific molecular markers for tomato bacterial spot resistance gene in tomato.
- Seed quality and seedling production technology research and development
- Construction of a certification system for plant seeds and seedlings─Establishment of molecular testing method for hybrid seed purity in pepper
- Study on Seed Vigor Detection Technology and Safe Storage Mode of Important Crops
- Intensification of Plant New Variety DUS Testing Technology and Research on Genetic Resources Management of the Potential Crop in Taiwan
- Export potential bulb flowers breeding and establishing the propagation system
- Breeding and Critical Techniques Development of Orchids.
- Breeding and evaluation of cucumber’s rootstock on water utilizing efficiency
- Study on producing cereal renewable pots and its effects on seedling production.
- Breeding for disease resistance in tomato and high quality eggplant.
- Breeding for Cucurbitaceae vegetables
- Breeding of high quality papaya varieties with international competitiveness
- Research on organic seed production of grain crops
- Establish a digital platform for seed illustration
- The performance evaluation and working tendency analysis for the seedling training courses in Farmers' Academy
- Enhancing industry connection of seed testing and international cooperation of ISTA
- 2018 Taiwan-Vietnam Plant Variety Protection Cooperation and Study on DUS Testing
- Study and Exchange on Plant Variety Protection System and DUS Testing Techniques between Taiwan and Indonesia
- Establishment of grafting technique and grafted seedling propagation system for oiltea camellia.
- Established qualitative detection method for unauthorized genetically modified orange petunias.
- Study of inspection acts for imported genetically modified feed and industrial applications traceability and export agricultural products
- Cacao breeding and development of vegetative propagation techniques
- Combine Tolerance of Papaya Ring Spot Viral Disease with All Hermaphroditic Character in Papaya Commercial Cultivar Adding Commercial Value.
- Establishment of foundation seed propagation system for potato variety‘Lunwei No.1’and‘Lunwei No.2’.
 Home > Achievement > 2018 Research Project List > The establishment and application of specific molecular markers to detect bacterial wilt resistance gene in tomato. Home > Achievement > 2018 Research Project List > The establishment and application of specific molecular markers to detect bacterial wilt resistance gene in tomato. |
The establishment and application of specific molecular markers to detect bacterial wilt resistance gene in tomato.
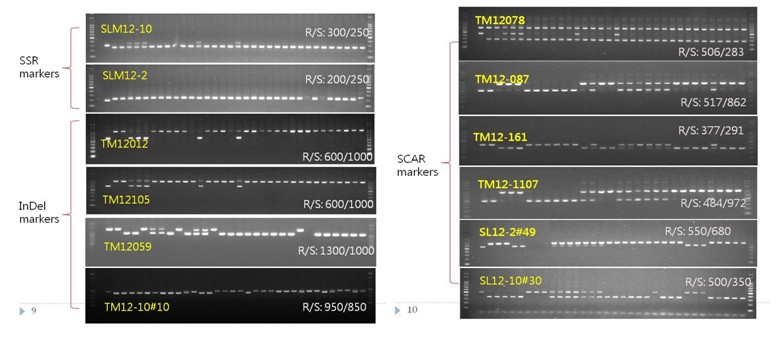
▲Fig. 1. TILLING was used to explore SNPs in the target segment. Four InDel markers (TM12012, TM12105,
TM12059, and TM12-10#10) and 6 SCAR markers were developed and screened. The stability of the primers
was tested by different tomato materials, and all the bands of resistant and susceptible genotypes were
stably amplified.
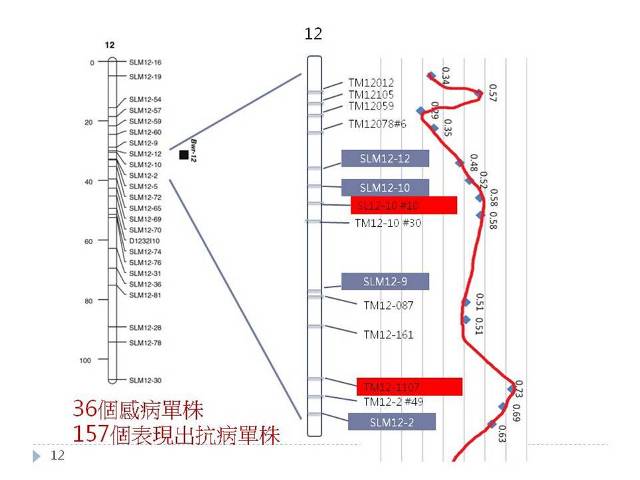
▲Fig. 2 The markers developed in this study for tomato bacterial wilt resistance gene
Bwr-12 were marked on the their relevant positions on the GeneBank HG975224.1
sequence from the NCBI database. The association between the genotypes of the markers
and the phenotypes were evaluated by 36 susceptible plants and 157 non-infected plants.
The marker, TM12-1107, which has the highest association could replace the reference
primers to detect the resistance gene.
