- Establishment of friendly cultivation module for cocoa seedlings
- Analysis of the arrangement of Nectar Plants under the Climate Change.
- Establishment of resilience cultivation practices by increase drought-tolerant of potato and ensure the production of leafy vegetables after typhoon destructed and rain disaster
- Research on Improving Agricultural Workers' Adaptation Strategies in Response to Climate Change: A Case Study of Agricultural Workers in Seedling production industries.
- Research on processing technology for reducing the waste of domestic agricultural production
- Establishment of techniques to reduce waste and create valueadded utilization of tomato seed processing by-producet and seasonal overproduced tomato.
- Establish the system of value-added utilization on pumpkin residues from seedling industry
- Development of value-added products from seeded papaya wastes
- Developement of eco-friendly nursery material technology
- Application of Herbal Medicine Plants in Animal Feed Additives and Establishment of GAP Production System.
- Construction and promotion of organic demonstration nursery
- Study on the development and industrial value of biochar which made by used media of mushroom
- Development of disinfection technique for important seed-borne pathogens of vegetables
- Research and application of value-added and waste reduction technology in green supply chain
- Construction of Intelligent Production and Sale Management Network for Vegetable Nursery
- Establishment of physiological parameters and production operation mode for vegetable nursery
- Modular development and application of production management information system in plant tissue culture
- The establishment of high through-put sequencing workflow to detect pathogens of tomato seeds
- Establishment of organic seed production and supplying system for grain crops
- Using seed priming treatment to promote crop stress tolerance and survey industry status
- Establishment of highly effective isolated facility for healthy seedling
- Development and application of molecular markers for the important traits of Solanaceae crops
- Development of potyvirus resistance in melon using CRISPR/Cas9 technology
- The Study of Healthy Seedling Production by In-vitro Micropropagation
- Research on optimization of detecting operation procedure for seed-borne pathogens
- Study and improvement of strengthening seed testing technology
- Strengthen Plant New Variety DUS Testing Techniques and Research on Genetic Resources Management and Application of the Potential Crops in Taiwan
- Breeding and key techniques research on orchids and bulb flowers
- Breed and assess the drought tolerance rootstocks with cucumber
- Breeding for disease resistant tomato and superior quality eggplant.
- Breeding for environment tolerance and high quality of Cucurbitaceae vegetables.
- Breeding of high quality papaya varieties with international competitiveness
- Establishment of environmentally friendly seed production system for grain crops
- Establish a digital platform for seed illustration
- Establishment of automatic seedling evaluation system and integration of seed testing platform
- Intelligent Marketing and Promotion of Seedling Production and Marketing Information Management System.
- Establishment of Phalaenopsis Varieties Identification and Application Integration Platform
- Research on the Integrated Planning and working tendency analysis for the seedling training courses in Farmers' Academy.
- Harmonization and Cooperation on DUS testing between Taiwan and Japan
- Taiwan-Israel Plant Variety Protection Cooperation and Study on DUS Testing
- Enhancing the seed testing technical cooperation with ISTA and new southbound countries
- Establishment of inspection and monitoring system for new era genetically modified organisms
- Study of inspection acts for imported genetically modified feed and industrial applications traceability and export agricultural products
 Home > Achievement > 2020 Research Project List > Development and application of molecular markers for the important traits of Solanaceae crops Home > Achievement > 2020 Research Project List > Development and application of molecular markers for the important traits of Solanaceae crops |
Development and application of molecular markers for the important traits of Solanaceae crops
c

▲Fig. 1. Tomato bacterial wilt is a soil-borne disease caused by Ralstonia solanacearum Smith. Although the infected plants remain green, they wither and die quickly. A cross section of an infected stem shows a brown discoloration of the vascular tissue and milky sticky bacteria mud exudates.
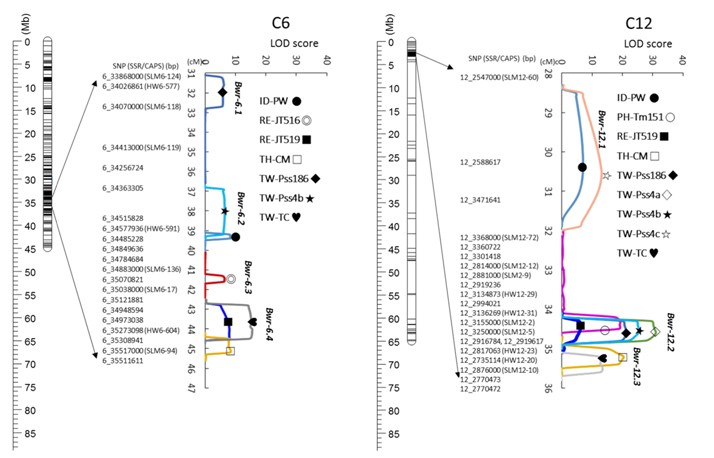
▲Fig 2. Shin et al. (2020) conducted a QTL resistance locus study on Hawaii7996, which has stable resistance to tomato bacterial wilt. The results showed that there are four QTLs on chromosome 6 and three QTLs on chromosome 12. The resistance of QTLs on chromosome 6 to tomato bacterial wilt pathogen is not as good as the QTLs on chromosome 12, but it has wider resistance and can tolerate endemic strains in different regions.
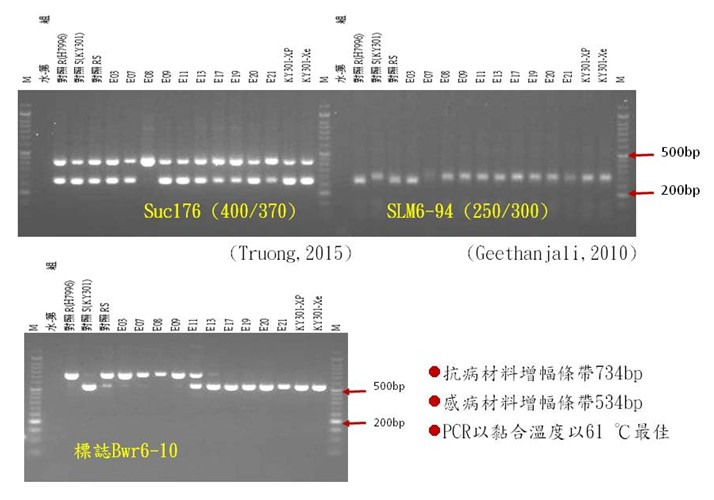
▲Fig 3. The marker Bwr6-10 developed for the resistance gene of tomato bacterial wilt on chromosome 6 is polymorphic in resistance to susceptible materials, increasing by 734bp and 534bp bands respectively, which is clearer and easier to interpret than the literature.
(b.) Development of the molecular marker for male sterility and fertility restorer in Capsicum Annuum L.
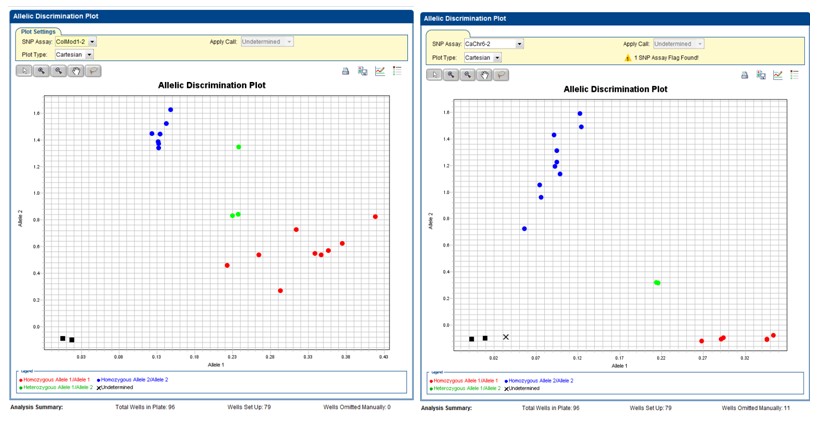
▲Fig 1. Fig 1. The genotyping result of real-time PCR of KASP assay for detecting fertility restorer (Rf) gene in pepper. The CaChr6-2 (right) developed in this study has a better cluster result than the reference SNP site, ColMod1 (left).
