- Establishment of friendly cultivation module for cocoa seedlings
- Analysis of the arrangement of Nectar Plants under the Climate Change.
- Establishment of resilience cultivation practices by increase drought-tolerant of potato and ensure the production of leafy vegetables after typhoon destructed and rain disaster
- Research on Improving Agricultural Workers' Adaptation Strategies in Response to Climate Change: A Case Study of Agricultural Workers in Seedling production industries.
- Research on processing technology for reducing the waste of domestic agricultural production
- Establishment of techniques to reduce waste and create valueadded utilization of tomato seed processing by-producet and seasonal overproduced tomato.
- Establish the system of value-added utilization on pumpkin residues from seedling industry
- Development of value-added products from seeded papaya wastes
- Developement of eco-friendly nursery material technology
- Application of Herbal Medicine Plants in Animal Feed Additives and Establishment of GAP Production System.
- Construction and promotion of organic demonstration nursery
- Study on the development and industrial value of biochar which made by used media of mushroom
- Development of disinfection technique for important seed-borne pathogens of vegetables
- Research and application of value-added and waste reduction technology in green supply chain
- Construction of Intelligent Production and Sale Management Network for Vegetable Nursery
- Establishment of physiological parameters and production operation mode for vegetable nursery
- Modular development and application of production management information system in plant tissue culture
- The establishment of high through-put sequencing workflow to detect pathogens of tomato seeds
- Establishment of organic seed production and supplying system for grain crops
- Using seed priming treatment to promote crop stress tolerance and survey industry status
- Establishment of highly effective isolated facility for healthy seedling
- Development and application of molecular markers for the important traits of Solanaceae crops
- Development of potyvirus resistance in melon using CRISPR/Cas9 technology
- The Study of Healthy Seedling Production by In-vitro Micropropagation
- Research on optimization of detecting operation procedure for seed-borne pathogens
- Study and improvement of strengthening seed testing technology
- Strengthen Plant New Variety DUS Testing Techniques and Research on Genetic Resources Management and Application of the Potential Crops in Taiwan
- Breeding and key techniques research on orchids and bulb flowers
- Breed and assess the drought tolerance rootstocks with cucumber
- Breeding for disease resistant tomato and superior quality eggplant.
- Breeding for environment tolerance and high quality of Cucurbitaceae vegetables.
- Breeding of high quality papaya varieties with international competitiveness
- Establishment of environmentally friendly seed production system for grain crops
- Establish a digital platform for seed illustration
- Establishment of automatic seedling evaluation system and integration of seed testing platform
- Intelligent Marketing and Promotion of Seedling Production and Marketing Information Management System.
- Establishment of Phalaenopsis Varieties Identification and Application Integration Platform
- Research on the Integrated Planning and working tendency analysis for the seedling training courses in Farmers' Academy.
- Harmonization and Cooperation on DUS testing between Taiwan and Japan
- Taiwan-Israel Plant Variety Protection Cooperation and Study on DUS Testing
- Enhancing the seed testing technical cooperation with ISTA and new southbound countries
- Establishment of inspection and monitoring system for new era genetically modified organisms
- Study of inspection acts for imported genetically modified feed and industrial applications traceability and export agricultural products
 Home > Achievement > 2020 Research Project List > Developement of eco-friendly nursery material technology Home > Achievement > 2020 Research Project List > Developement of eco-friendly nursery material technology |
Developement of eco-friendly nursery material technology
To reduce the usage and pollution of plastic containers in the nursery industry, this experiment studies using the lifespan of degradable polylactic acid (PLA) containers for nursery production and the optimum condition of container degradation. The results showed that different storage methods did not significantly affect the use efficacy of nursery materials in the short term, but the ultimate tensile strength of nursery bags for long-term storage decreased and accelerated its degradable rate in the soil. Temperature and humidity both affected the degradable rate of polylactic acid nursery materials in the soil. The degradable rate when buried in the soil is the fastest under the conditions of high temperature and high humidity. In the insect feeding test, the decomposition rate is faster when the insect grows at a suitable temperature. The weight loss is as high as 27% after 14 days. The type of insect's mouthparts may affect the types of nursery materials that can be gnawed. In the future, high-protein feed insects for aquaculture, poultry or livestock can be evaluated to solve the waste disposal problem. The results will help the industry to improve the performance of degradable containers and achieve reductions of carbon emission and plastic waste. Finally, the study will benefit the nursery industry by adoption of the sustainable practices.
|
環境因子 |
聚乳酸育苗資材 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
白色 |
白色 |
黑色 |
|
|
溫度 |
***y |
** |
*** |
|
濕度 |
*** |
* |
ns |
|
溫度×濕度 |
*** |
ns |
ns |
y:ns,*,**,***:indicated nonsignificant or significant at p≦0.05, 0.01 or <0.001, respectively.
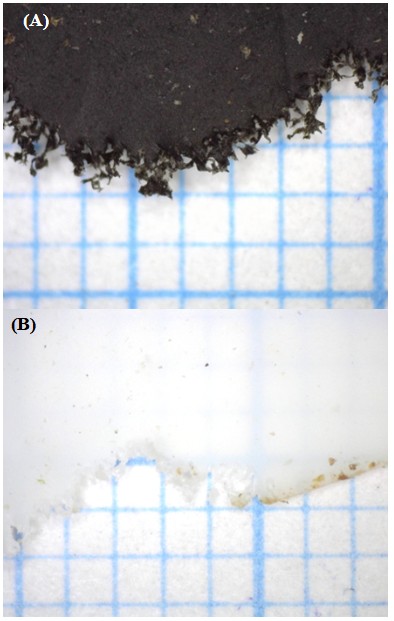
▲Fig.1. the polylactic acid containers (A)black polylactic
acid seedling bags and (B) white polylactic acid plugs
are gnawed by Zophobas morio.
