- Research on Seedling Propagation Technology of Eastern Aboriginal Tribes
- Counseling on Digital Transformation of Small,Medium and Micro-sized Crops and Seedlings with Potential for Export
- Recycling of surplus materials from tomato and pumpkin productio
- Research on the improvement of a renewable energy supply chain model for the residual media of mushroom
- Adaptation and mitigation the impact of important weeds on staple crops (cucumber) under climate change
- Constructing intelligent identification services for seed and seedling industry
- Application and Promotion of Production and Sales Management Wisdom Network for Vegetable Nursery
- Function Demonstration and Optimization of the Expert System for Vegetable Seedling Production Forecast
- The establishment of smart production and application model of plant tissue culture
- Research of optimization for detecting operation procedure on seed-borne pathogens and development of seed disinfection technique
- Research and consulting on the response of seed industry under high temperature and drought stress.
- Establishment of the heat-resistant selection index and breeding of tomato
- High quality tomato and stress tolerance breeding technology in Facility.
- Evaluation and Application of Drought-tolerant Potato Germplasm Resources
- Establishment of the biological indicator of disease resistance for tomato in drought condition
- Establishment of marker assisted selection applied to the selection of drought-tolerant maize and heattolerant tomato
- Establishment of precise and efficient breeding technology for industry-oriented traits of cauliflower
- Molecular Marker-Assisted Tomato Disease Resistance Breeding Selection Model Construction and Technology Development
- Participatory Selection of Healthy Ginger Seedlings and Establishment of Production System
- Participatory selection of taro regional clonal lines
- Analysis and application of root‐associated microbes from soil-borne disease resistant and sensitive lines of Solanaceae crops
- Improvement on the Micropropagation Technique - In vitro propagation of avocado (Persea americana Mill.) through apical buds and nodal segments
- Developing of crops novel assisted breeding technology on melon
- Research on germplasm maintenance and industrial application of vegetative propagation crops
- Germplasm development and application of Aeridinae subtribe orchids and Cattleya genus.
- The Establishment of Organic Seedling and Seed Saving System
- Research on Genetic Resources and Plant New Variety DUS Testing Techniques Management and Application of the Economical and Special Crops in Taiwan
- Establishment of organic seed production and supplying system for grain crops
- The seedling leaf electrolyte leakage index was used to select papaya heat-resistant Resistance and virus Resistance varieties.
- Selecting for resistance bacterial wilt and F1 Seed Collection of tomato.
- Techniques development for bulb flowers breeding
- Establish Cucurbitaceae vegetable breeding technologies of heat tolerance
- Establishing the Technology ofNew Papaya Viety Breeding for the International Market.
- Research on Agricultural Social Responsibility for the trainees of Farmers' Academy
- Establishment of Phalaenopsis Varieties Identification and Application Integration Platform
- Study of inspection and monitoring system for precisely breeding crops
- Harmonization and Cooperation on DUS testing between Taiwan and Japan
- Taiwan-Israel Plant Variety Protection Cooperation and Study on DUS Testing
 Home > Achievement > 2022 Research Project List > Research of optimization for detecting operation procedure on seed-borne pathogens and development of seed disinfection technique Home > Achievement > 2022 Research Project List > Research of optimization for detecting operation procedure on seed-borne pathogens and development of seed disinfection technique |
Research of optimization for detecting operation procedure on seed-borne pathogens and development of seed disinfection technique
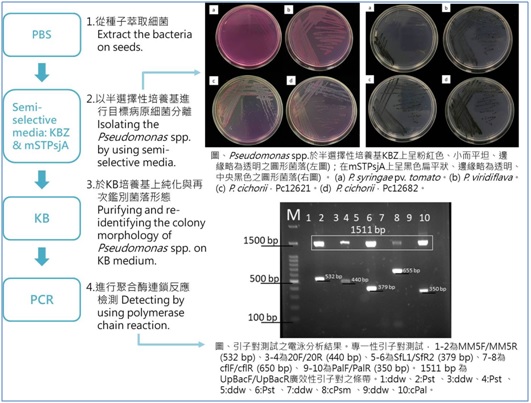
Pseudomonas spp. are important bacterial plant pathogens and are valued in international seed trade market owing to their seed transmission. The goal of this study was to establish an integrated operating procedure for detecting five Pseudomonas spp., including P. syringae pv. tomato (Pst), P. viridiflava (Pv), P. cichorii (Pc), P. syringae pv. maculicola (Psm) and P. syringae pv. lachrymans (Pal) on Solanaceae seeds in order to improve efficiency and to decrease costs. Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) was first used for extract bacteria from seeds. Then, suspected bacteria were isolated by using semi-selective media. Finally, five specific primers, including MM5F/MM5R (for Pst), 20F/20R (Pv), SfL1/SfR2 (for Pc), cflF/cflR (for Psm and Pst) and PalF/PalR (for Pal), were adopted to identify the Pseudomonas spp. individually.